The Vital Role of Physiotherapists in Managing Arthritis and Knee Ligament Injuries
Introduction:
At the centre of Mohali is a home for hope and healing. Brar’s Physio Care is a place of deliverance where Dr. Lakhveer Singh provides for many people with acute arthritis and knee ligament injuries who suffer from their disease.
The Scope of Arthritis and Knee Ligament Injuries:
Arthritis – clinical status and quality of life. Overall, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 350 million people have arthritis, and among them, osteoarthritis accounts for the vast majority of cases. It is worrying that in India such numbers are also high as about 15% of the population or 180 million people have arthritis.
Injury to the knee ligaments is equally relevant, but injury to the ACL is very common. Research carried out suggests that athletes are primary victims of ACL injuries with the incidence rate being 68. 6/100,000 of person-years in the general population and 200,000 cases per year in the United States.
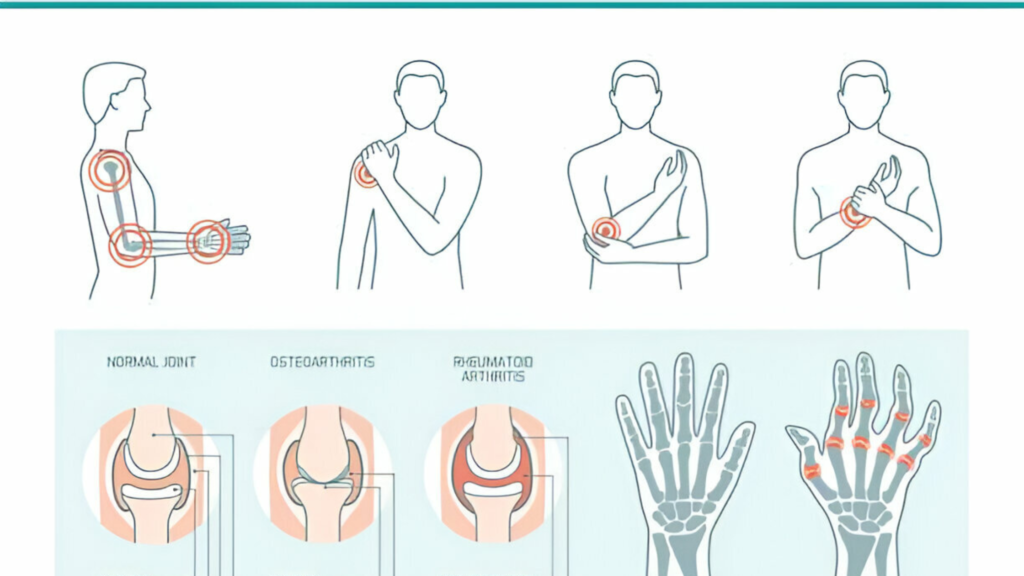
The Role of Physiotherapy in Managing Arthritis:
- Pain Relief and Mobility Enhancement: Physiotherapy is instrumental in alleviating pain and enhancing mobility for arthritis patients. Techniques such as manual therapy, exercise regimens, and the use of modalities like ultrasound and electrical stimulation are commonly employed. A study published in the Journal of Rheumatology found that patients undergoing physiotherapy for osteoarthritis reported a 20% to 30% reduction in pain and a significant improvement in joint function.
- Personalized Exercise Programs: Physiotherapists design personalized exercise programs that strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint stability. Research shows that regular, targeted exercise can reduce arthritis symptoms by up to 50%.
- Education and Self-Management: Education plays a vital role in arthritis management. Physiotherapists at Brar’s Physio Care empower patients with knowledge about their condition and teach them self-management strategies to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Managing Knee Ligament Injuries:
- Rehabilitation and Functional Recovery: Following knee ligament injuries, especially ACL tears, physiotherapy is critical for rehabilitation. A comprehensive rehabilitation program typically involves progressive strengthening exercises, balance training, and functional activities designed to restore knee stability and function. Studies indicate that patients who adhere to structured physiotherapy programs have better outcomes, with return-to-sport rates as high as 82%.
- Prevention of Re-Injury: As the best physiotherapist in Mohali, Dr. Lakhveer Singh focuses not only on recovery but also on preventing re-injury. This involves educating patients about proper techniques, conducting sport-specific training, and implementing neuromuscular training programs. Evidence suggests that such preventative strategies can reduce the risk of recurrent ACL injuries by up to 50%.
- Holistic Approach: The holistic approach adopted at Brar’s Physio Care includes psychological support, nutritional advice, and lifestyle modifications, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their unique needs.

FAQs on Arthritis and Knee Ligament Injuries with the Best Physiotherapist in the City:
What are the specific techniques used in physiotherapy for managing arthritis?
Several intervention strategies do exist in physiotherapy in the management of arthritis including pain relief, joint mobility, and the general well-being of the affected patient. Here are some specific techniques commonly used:
Exercise Therapy
Types of Exercises:
- Range-of-Motion Exercises: These exercises help maintain or increase joint flexibility. Examples include gentle stretching and movements that take the joint through its full range of motion.
- Strengthening Exercises: Building muscle strength around affected joints helps provide better support and reduces stress on the joint. This can include resistance training with bands, weights, or body weight.
- Aerobic Exercises: Low-impact activities such as walking, cycling, and swimming improve cardiovascular health without putting undue stress on the joints.
Evidence: Studies show that exercise can significantly reduce pain and improve function in arthritis patients.
Manual Therapy
- Joint Mobilization: This involves the physiotherapist using their hands to apply gentle, controlled movements to the joint to improve mobility and decrease pain.
- Soft Tissue Mobilization: Techniques such as massage help relax tense muscles, improve circulation, and reduce pain around the affected joints.
Evidence: Manual therapy has been found effective in managing pain and improving physical function in arthritis patients.
Heat and Cold Therapy
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat can help relax muscles and increase blood flow to the affected area, reducing stiffness and pain. Methods include hot packs, warm baths, or heating pads.
- Cold Therapy: Applying cold can help reduce inflammation, swelling, and pain. Methods include ice packs or cold baths.
Evidence: Heat and cold therapy are commonly recommended for symptom relief in arthritis management.
Electrotherapy
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): This involves using low-voltage electrical currents to provide pain relief.
- Ultrasound Therapy: High-frequency sound waves are used to reduce pain and inflammation and promote tissue healing.
Evidence: Electrotherapy modalities like TENS and ultrasound have been shown to reduce pain and improve function in arthritis patients.
Hydrotherapy
- Aquatic Exercises: Exercising in warm water reduces the strain on joints while providing resistance for strength training. This is especially beneficial for individuals with severe arthritis who find land-based exercises too painful.
Evidence: Hydrotherapy has been proven to improve pain, strength, and quality of life in individuals with arthritis.
- Assistive Devices and Education
- Education on Joint Protection: Physiotherapists teach techniques to avoid excessive joint stress during daily activities.
- Use of Assistive Devices: Devices such as splints, braces, or orthotics can help support affected joints, reducing pain and improving function.
Evidence: Proper use of assistive devices and education significantly help in managing arthritis symptoms and maintaining function.
Balance and Coordination Training
Improving balance and coordination can help prevent falls and improve the overall functional ability of arthritis patients. This can include exercises like standing on one leg, using balance boards, and practicing gait training.
Evidence: Balance and coordination training are important components of comprehensive arthritis management, improving overall stability and function
What are the specific techniques used in physiotherapy for managing knee ligament injuries?
Knee ligament injury management using physiotherapy applications aims at relieving pain and improving deformity as well as reducing the chances of re-injury. Here are some specific techniques commonly used:
Exercise Therapy
Types of Exercises:
- Range-of-Motion Exercises: To restore flexibility and mobility in the knee joint. Examples include heel slides and knee bends.
- Strengthening Exercises: Focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings. Exercises might include leg presses, squats, and lunges.
- Proprioception and Balance Exercises: To improve stability and prevent future injuries. Balance boards, single-leg stands, and wobble boards are often used.
Evidence: Exercise therapy is crucial for rehabilitation after knee ligament injuries, significantly improving strength, stability, and overall knee function.
Manual Therapy
- Joint Mobilizations: Techniques to improve joint motion and reduce pain. Physiotherapists may use gentle gliding and stretching movements.
- Soft Tissue Mobilization: Massage and other manual techniques to reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and decrease swelling.
Evidence: Manual therapy, combined with exercise, enhances outcomes for patients with knee ligament injuries.
Cryotherapy and Thermotherapy
- Cryotherapy (Cold Therapy): Application of ice packs or cold compresses to reduce inflammation and pain immediately following injury.
- Thermotherapy (Heat Therapy): Use of heat packs to relax muscles and increase blood flow during the later stages of rehabilitation.
Evidence: Cold and heat therapies are effective in managing pain and inflammation during different stages of recovery.
Electrotherapy
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Uses electrical currents to reduce pain and improve muscle function.
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES): Helps stimulate muscle contractions, particularly useful in early rehabilitation to maintain muscle mass and strength.
Evidence: Electrotherapy can reduce pain and enhance muscle reactivation in knee ligament injury rehabilitation.
Functional Training
- Gait Training: Techniques to restore normal walking patterns, including weight-bearing exercises and treadmill walking.
- Sport-Specific Drills: For athletes, drills that mimic sports movements to prepare the knee for return to play.
Evidence: Functional training is critical for ensuring a successful return to daily activities and sports.
Bracing and Taping
- Knee Bracing: Provides support and stability to the knee, particularly useful during the initial healing phase or high-risk activities.
- Kinesiology Taping: Helps reduce pain, improve circulation, and support the muscles around the knee.
Evidence: Bracing and taping can provide additional support and improve proprioception during the rehabilitation process.
Hydrotherapy
- Aquatic Exercises: Performing exercises in water to reduce stress on the knee while maintaining resistance for muscle strengthening.
Evidence: Hydrotherapy reduces pain and improves joint function in a low-impact environment.
How does Brar’s Physio Care provide our patients with psychological support, nutritional advice, and lifestyle modifications?
One of the strategies that Dr. Lakhveer Singh at Brar’s Physio Care adopts toward patient care is focusing on the mental health and diet of the patient. Here’s how we integrate these elements into their treatment plans:
Psychological Support
Approach:
- Counseling Sessions: Brar’s Physio Care offers one-on-one counseling sessions with trained psychologists to help patients cope with the emotional and mental stress associated with injuries or chronic conditions.
- Support Groups: We facilitate support groups where patients can share their experiences and gain encouragement from others facing similar challenges.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises are integrated into the rehabilitation programs to help manage pain and reduce stress.
Benefits:
- Psychological support helps improve patients’ overall mental well-being, which can enhance recovery outcomes.
- Counseling and support groups provide a platform for patients to express their concerns and receive validation and support.
Nutritional Advice
Approach:
- Personalized Nutrition Plans: Brar’s Physio Care collaborates with nutritionists to create personalized diet plans that cater to the specific needs of patients, whether for injury recovery, weight management, or chronic disease management.
- Education on Balanced Diet: Patients are educated on the importance of a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients that support healing and overall health.
- Supplements Guidance: Advice on the use of supplements to ensure patients receive adequate vitamins and minerals necessary for recovery.
Benefits:
- Proper nutrition supports tissue repair, reduces inflammation, and enhances energy levels, all of which are crucial for effective rehabilitation.
- Personalized nutrition plans ensure that dietary recommendations are tailored to the unique needs and health conditions of each patient.
Lifestyle Modifications
Approach:
- Exercise Programs: Tailored exercise programs are designed to fit into patients’ daily routines, promoting long-term adherence and lifestyle change.
- Ergonomic Advice: Guidance on proper posture and ergonomics at work and home to prevent further injury and manage pain.
- Health Education: Providing information on healthy lifestyle choices, including smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, and stress management techniques.
Benefits:
- Implementing lifestyle changes helps prevent the recurrence of injuries and manage chronic conditions effectively.
- Ergonomic advice and exercise programs improve overall physical health and functionality, reducing the risk of future complications.

Conclusion:
Knee physiotherapy is necessary to treat and control arthritis and knee ligament injuries. Dr. Lakhveer Singh at Brar’s Physio Care puts his efforts into the betterment of human health by easing the pains of muscles, finding the right remedies, rehabilitating, providing educative centres, and implementing preventive measures. We provide the local population with a wide range of services, from physical therapy to rehabilitation.
Strategic interventions on the part of the rehabilitation centres can cover psychological health, dietary, and lifestyle practices to ensure that their patients have holistic recovery and help them achieve sustained health and wellness. This type of care helps in recovering from a disease or condition faster as well as improving general health and welfare for their patients.
Knee ligament injury is treated using a culmination of rest, exercise, manual and electrotherapy exercises, functional training, and wrist and ankle braces. Rehabilitation interventions that are targeted at a specific injury or patient for their individual needs to promote recovery and return to function.